Getting Started Enterprise
Enabling the Weave Policy Engine features in Weave GitOps is done by running the policy agent on the cluster. This section gives an overview of the policy ecosystem and the steps required for installing and running the policy agent on leaf clusters.
The Policy Ecosystem
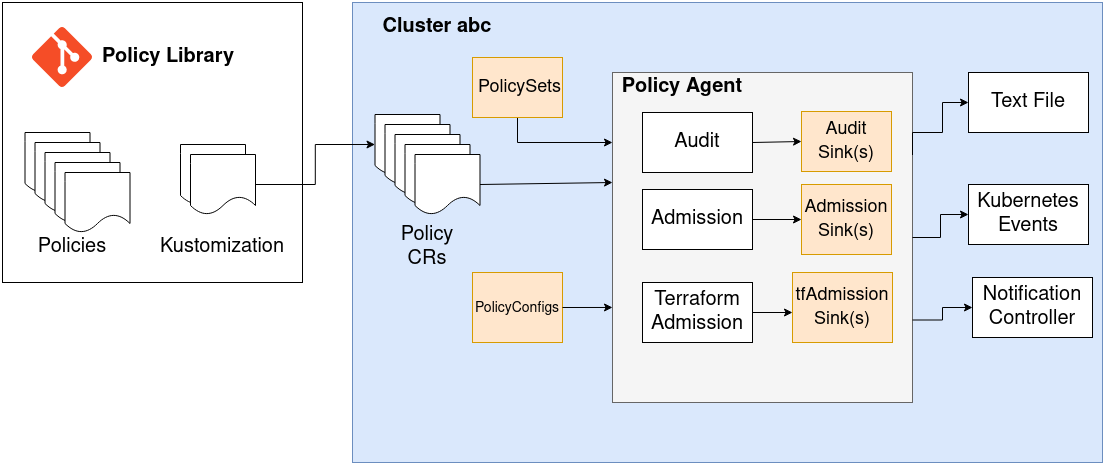
The policy ecosystem consists of several moving parts. The two primary components are the Policy Agent and the Policy CRs. The agent runs in several modes, and uses the Policy CRs to perform validations on different resources. The results of those validations can be written to different sinks.
There are two other optional components: the PolicySet, and the PolicyConfig. The PolicySet can be used to filter policies for a specific mode, while the PolicyConfig can be used to override policy parameters during the validation of a certain resource.
Installation Pre-requisites
Weave GitOps
You need to have a running instance of Weave GitOps with at least one CAPI provider installed to provision Kubernetes clusters. See Weave GitOps Installation page for more details about installing Weave GitOps.
Policy Library
For the policy agent to work, it will need a source for the policies that it will enforce in the cluster. Enterprise customers should request access to fork our policy library into their local repositories. Our policy library includes an extensive list of policy CRs that cover a multitude of security and compliance benchmarks.
Install the Policy Agent
To install the policy agent on a leaf cluster, you should select the weave-policy-agent from the profiles dropdown in the Create Cluster page.
You should then configure the values.yaml to pull the policies from your repo into the cluster. This is done by configuring the policySource section. If your policy library repo is private, you will also need to reference the Secret that contains the repo credentials. This is usually the secret you created while bootstrapping Flux on the management cluster and is copied to your leaf cluster during creation.
Expand to see an example that creates a new git source
policySource:
enabled: true
url: ssh://git@github.com/weaveworks/policy-library # This should be the url of the forked repo
tag: v1.0.0
path: ./ # Could be a path to the policies dir or a kustomization.yaml file
secretRef: my-pat # the name of the secret containing the repo credentials
Expand to see an example that uses an existing git source
policySource:
enabled: true
sourceRef: # Specify the name for an existing GitSource reference
kind: GitRepository
name: policy-library
namespace: flux-system
You can find more about other policy profile configurations here.
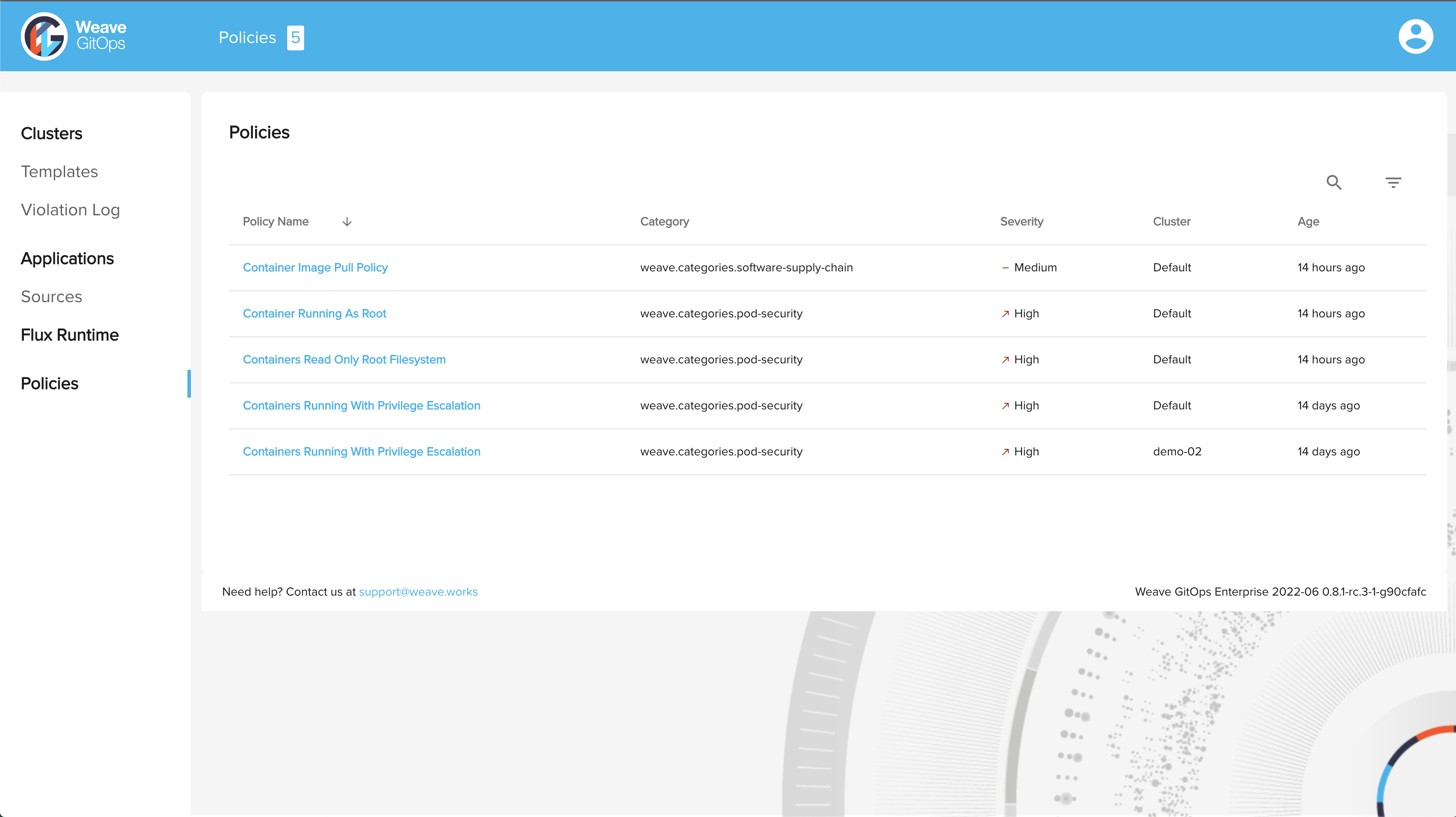
Policies in UI
After the leaf cluster is provisioned and the profile is installed, you should now see the policies listed in the Policies tab in Weave GitOps UI.
Now you have a provisioned cluster with these policies enforced by the policy agent.
By default, the policy profile is set up to enforce policies at deployment time using admission controller, which results in blocking any deployment that violates the enforced policies.
Prevent Violating Changes
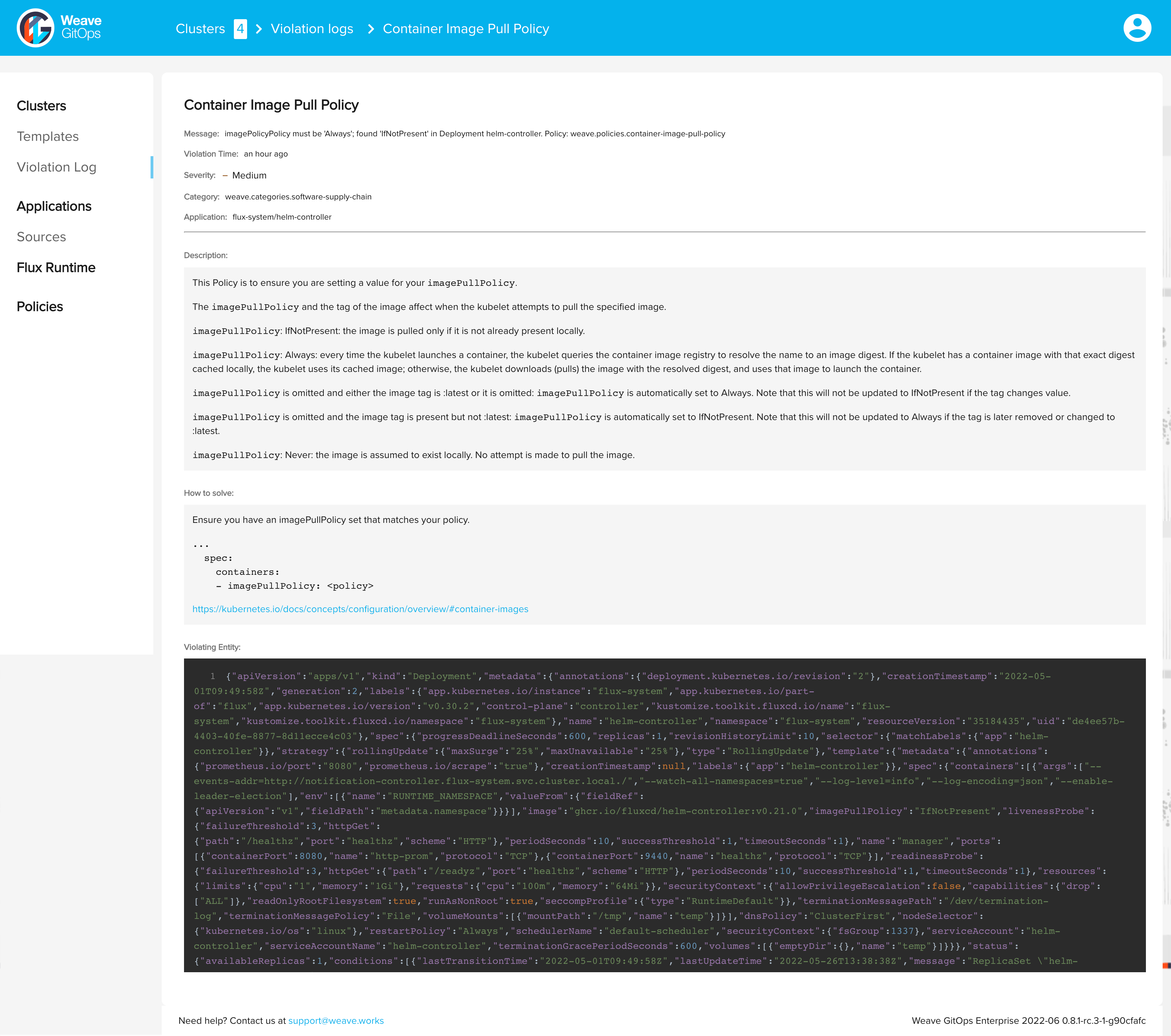
Now let's try to deploy a Kubernetes deployment that violates the Container Image Pull Policy which is one of the enforced policies.
This policy is violated when the container's imagePullPolicy is not set to Always.
Expand for an example of a violating deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Once you apply it, the policy agent will deny this request and show a violation message, and accordingly the deployment will not be created.
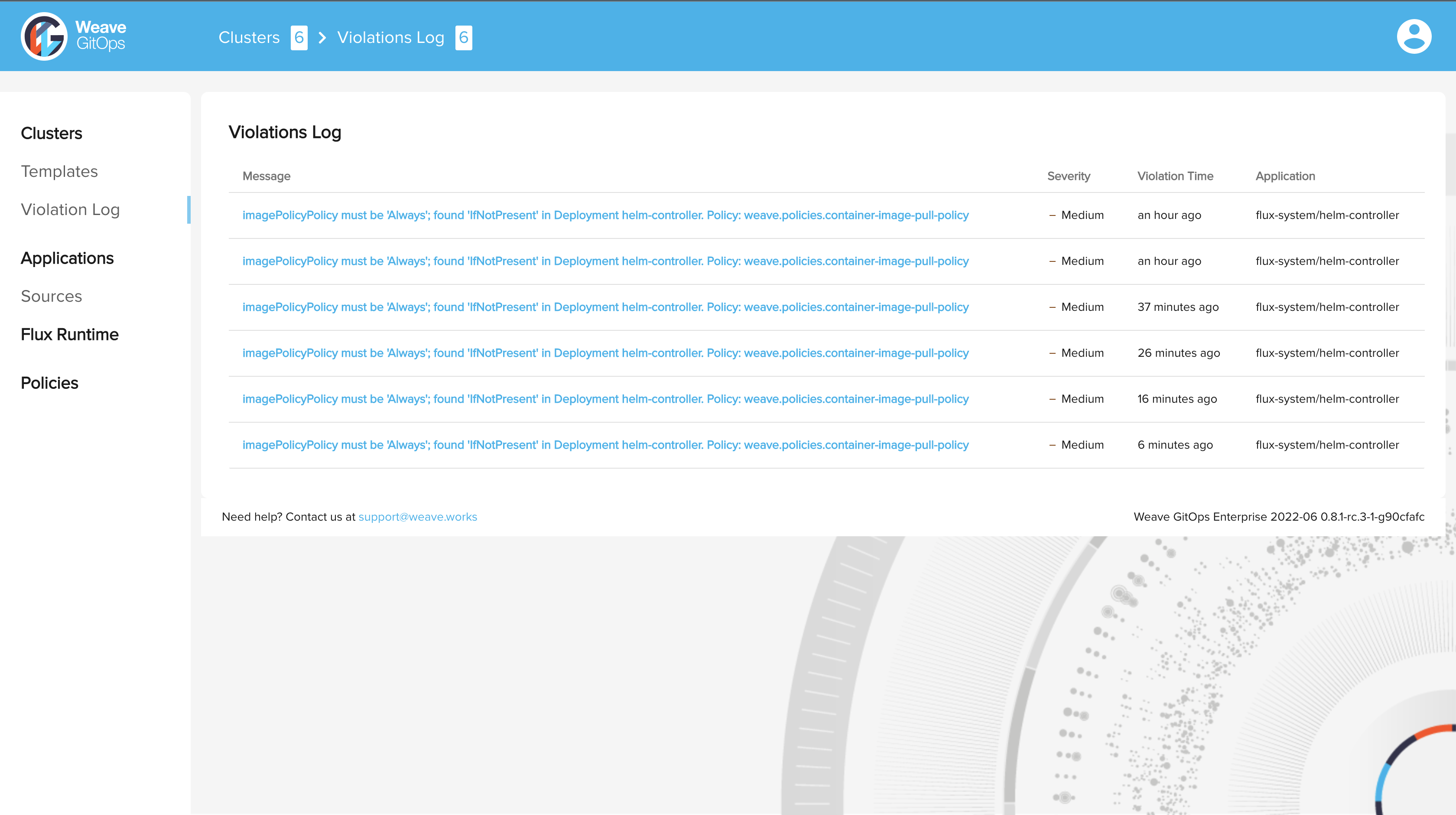
Violations Logs in UI
You can go to the Violations Log in Weave GitOps UI to view the policy violations of all the connected clusters, and dive into the details of each violation.
This view shows only the violations resulting from the admission mode by configuring the events sink.
Violations Log